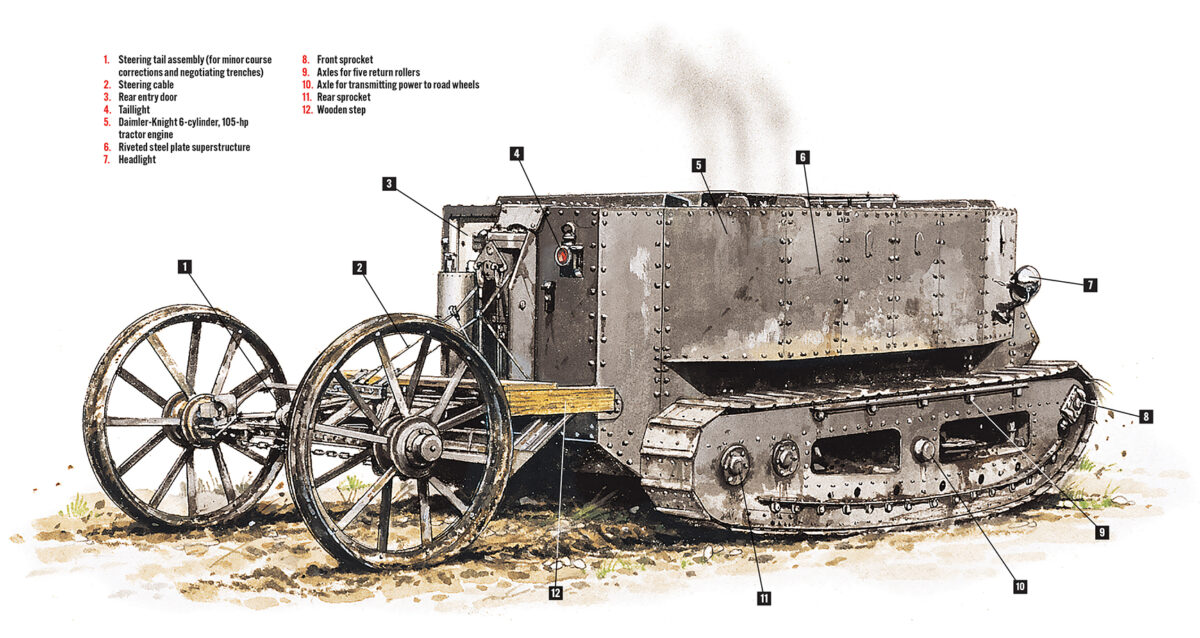
Specifications:
Length: 26 feet 6 inches
Height: 8 feet 3 inches
Width: 9 feet 5 inches
Track width: 20½ inches
Weight: 16 tons
Armor: 10 mm
Power: Rear-mounted Daimler-Knight 6-cylinder, 105 hp tractor engine
Maximum speed: 2 mph
Main armament: 2-pounder Vickers gun in rotating turret (not installed)
Crew: Five
When World War I settled into static trench warfare, even the most advanced armored cars were effectively immobilized by the Western Front’s combination of muddy terrain, trenches, barbed wire, heavy machine guns and artillery.
To meet such challenges, in February 1915 British First Lord of the Admiralty Winston Churchill formed a Landship Committee tasked with designing an armored vehicle capable of mastering mud, bridging an 8-foot gap, climbing a 5-foot earthwork and other specifications outlined by British army Lt. Col. Ernest Swinton. Under the guidance of mechanical engineer Major Walter Wilson of the Royal Naval Air Service and agricultural engineer Sir William Tritton, the committee purchased twin “creeping grip” track assemblies from the Bullock Tractor Co. of Chicago, Ill., and fitted them beneath a boxlike crew compartment of riveted steel plates. Powering the vehicle was a Daimler-Knight 6-cylinder, 105 hp tractor engine provided by Tritton’s Foster & Co., of Lincoln, England. On discovering the Bullock tracks were too small to accommodate the vehicle’s weight, Tritton designed longer, wider tracks. He also added twin rear wheels to facilitate steering. A proposed round turret packing a 2-pounder Vickers gun was never installed.
Officially known as the No.1 Lincoln Machine or Tritton Machine, the prototype landship was nicknamed “Little Willie” (a derisive name then applied to Crown Prince Wilhelm of Prussia). When not undergoing testing, it was kept under the strictest wraps, a backstory claiming it was a new mobile “water tank.” The abbreviated tank reference became universal for Little Willie’s descendants.
Little Willie was found to be top-heavy, but by that time a better design was in development, with a rhomboid-shaped track running above and below the superstructure and 6-pounder guns in sponsons on either side. Nicknamed “Mother,” the improved variant was further refined into the Mark I tank, which first saw combat at the Somme on Sept. 15, 1916. Today the tank’s forebear, Little Willie, is in the collection of the Tank Museum in Bovington, England.
This story appeared in the 2023 Autumn issue of Military History magazine.
historynet magazines
Our 9 best-selling history titles feature in-depth storytelling and iconic imagery to engage and inform on the people, the wars, and the events that shaped America and the world.