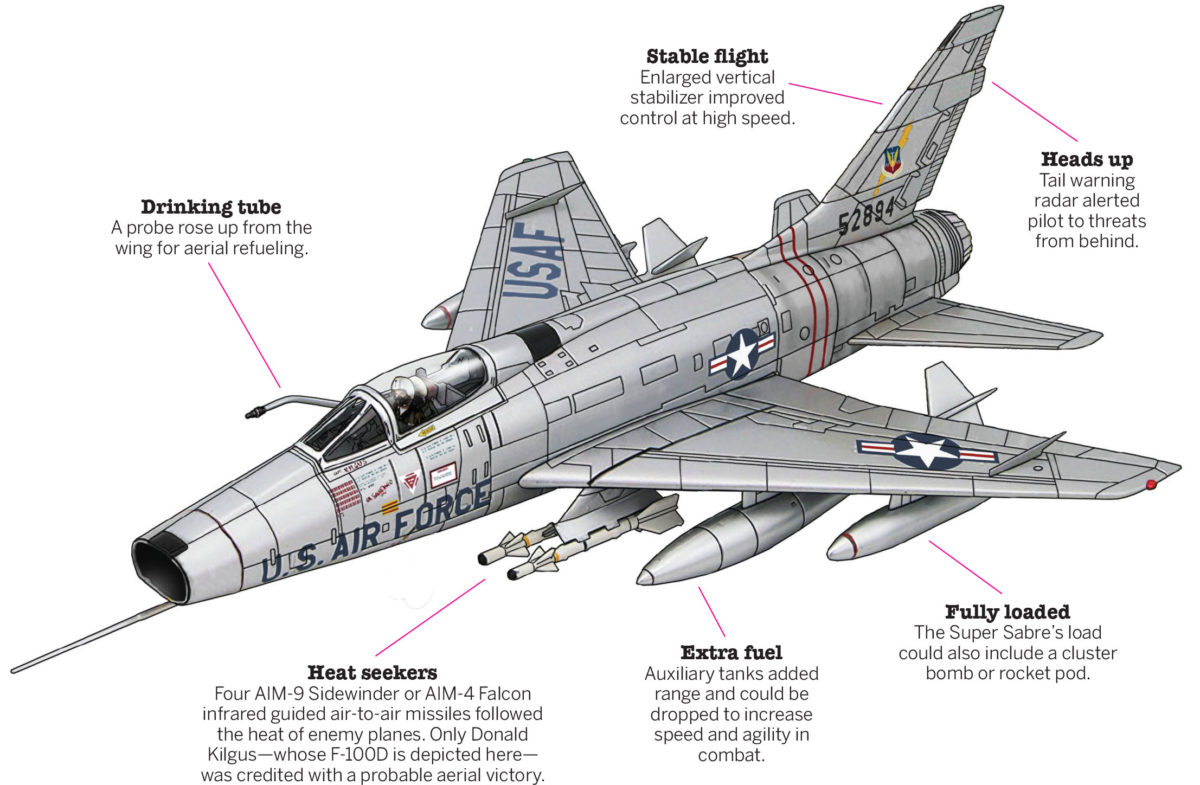
On April 16, 1961, six F-100D Super Sabres deployed to Thailand’s Don Muang Air Field, initiating the fighter-bomber’s 10-year deployment to Indochina. The plane was North American Aviation’s successor to its F-86 Sabre, famous for its exploits in the Korean War. The F-100, first flown in 1953, underwent many modifications. The F-100D, which entered service in September 1956, featured an enlarged wing and vertical stabilizer that provided better control at high speed, an autopilot, improved radio equipment and in-flight refueling capability. The jet also had additional flaps on the rear edge of the wing that increased stability and lowered the accident rate. The F-100D was the first fighter to incorporate a “buddy-store” refueling system, enabling it to refuel other F-100s in flight.
In its early combat missions, the F-100 escorted RF-101 Voodoos on reconnaissance flights over Laos in 1962 and F-105D Thunderchief fighter-bombers on strike missions to North Vietnam in 1965, Operation Rolling Thunder’s first year. The F-100D also laid claim to the Air Force’s first aerial victory over Vietnam with a probable shootdown of a North Vietnamese MiG-17 by Capt. Donald Kilgus on April 4, 1965.
The F-100D—or Hun, as it was more commonly called in a shortened form of “one hundred”—is best known for its close air support missions over South Vietnam. F-100Ds flew more than 70 percent of the Air Force’s close air support missions between 1965 and 1969. However, beginning in 1967 that role was increasingly filled by F-4 Phantom IIs, F-105s and A-7 Corsair IIs because of their greater payload, more accurate bombing system and longer loiter time. Designed for dogfighting and close air support in the era before electronic warfare and precision weapons, the Super Sabres departed Indochina in 1971 and retired from service in 1979. Super Sabres flew 360,283 combat sorties in the Vietnam War, and 242 were lost, most of them F-100Ds.
Engine: Pratt & Whitney J-57-P-21 turbojet with 16,000 lbs. of thrust
Wingspan: 38 ft., 9.37 in.
Length: 54 ft., 2 in.
Height: 16 ft., 2 in.
Max. weight: 37,124 lbs.
Max. speed: Mach 1.1
Combat radius: 511 nautical miles
Operating altitude: 43,500 ft.
Armament: Four M39 20 mm cannon; up to four AIM-9 Sidewinder air-to-air missiles
Bombload (typical): Two 750-lb. bombs; two 500-lb. bombs, rocket pods, cluster bomb units or napalm